How is Dyslexia Diagnosed?
There are four main methods for diagnosing dyslexia listed in the order they were developed. We use the Reading Skills Profile Method and explain the advantages of that method.
The Discrepancy Method
This method takes advantage of the fact that someone with dyslexia typically has great difficulty in learning to read but appears normal in other intellectual and educational activities. When there is a sufficiently large difference between reading and IQ test scores, one is diagnosed as having dyslexia.
Read More
Dyslexia is characterized by a difficulty in learning to read, but normal performance in other intellectual and academic areas. The discrepancy method of diagnosing dyslexia involves administering reading tests and general measures of intellectual performance (e.g., an IQ tests) and determining if there is a discrepancy between the two. That is, normal performance on the intelligence tests and poor performance on the reading test. The discrepancy procedure is the traditional way of identifying individuals with dyslexia. However, the discrepancy method has critical flaws and more modern procedures have been suggested as diagnostic procedures.
Response to Intervention (RTI)
Starting in first grade children are identified who are deficient in pre-reading skills that are important for the development of skilled reading. These children are then separated from peers and given focused group instruction in the missing skills. For a period of up to three years a student is given gradually increasing intensive instruction if they do not improve. After three years if the student is still well behind their peers the student is diagnosed as having dyslexia.
Read More
Response to Intervention is the procedure most commonly used in today’s school systems and is the procedure recommended by federal legislation. RTI involves screening all children at the first-grade level to identify children who are deficient in skills (e.g., phonological awareness, letter naming, letter sound naming) that are important for the development of skilled reading. These children are then separated from peers and given focused group instruction in missing skills.
Typically, in the second grade another screening test is administered and children who remain well behind peers are given another round of intense instruction (called best practice instruction), perhaps involving one-on-one instruction with a reading professional. This more intense level of instruction may continue through the third grade. If after three years of best practice instruction the child still is well behind peers in reading development the child is diagnosed as having dyslexia.
Reading Skills Profile Method
Reading Success Lab uses this method to diagnose dyslexia. This method involves a administering series of reading tasks to a student and comparing performance on these task to their peers. People with dyslexia have a very distinctive pattern of doing well on some but poorly on other tasks when compared to their peers. See this very distinctive pattern in the graph shown below, which shows grade level percentiles on a series of reading tasks. Almost all dyslexic people show this very distinctive pattern.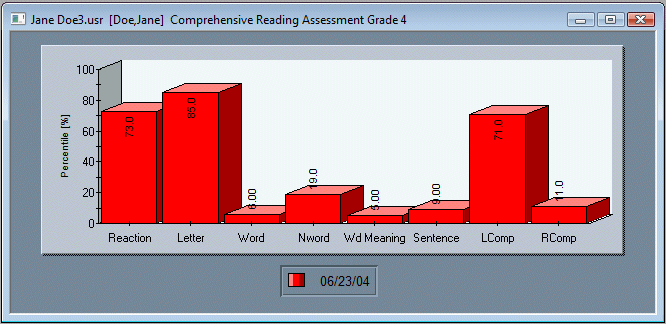
Read More
The Reading Success Lab software uses this method to diagnose dyslexia. This method involves a administering series of reading tasks and collecting speed and accuracy information of each item in the tasks. The speed and accuracy data is then transformed into grade level percentiles that show how a given student performs on the tasks relative to grade level peers.
Above is an image of from the Reading Success Lab diagnostic software. The graph shows the grade level percentile performance of a typical dyslexic child. The child has normal performance on tasks that measures the speed and accuracy of identifying stars and plusses (called a reaction task) and letters of the alphabet. However, the speed and accuracy performance on tasks that measure word identification, nonword identification, word meaning, sentence understanding and reading comprehension are well below average for grade level. Notice, however, that listening comprehension is perfectly normal. The software makes a diagnosis of dyslexia when this specific pattern of performance is present.
The Reading Skills Profile Method can also identify superior readers, average readers, poor readers who do not have dyslexia, readers who may have an attentional disorder, readers who may have a global cognitive deficit, and readers who likely have dyslexia.
Functional Magnetic Resonance Imagery (fMRI) Analyses
fMRI is a medical technique that allows a researcher to see what parts of the brain are active when an individual is reading. Individuals with dyslexia typically have different patterns of brain activation than do normal readers.
Read More
A final procedure that can be used to identify dyslexia is to take a child to a medical or research facility that can conduct fMRI analyses. fMRI is a medical technique that allows a researcher to see what parts of the brain are active when an individual is reading. Individuals with dyslexia typically have different patterns of brain activation than do normal readers, and this difference can be used to identify readers who are dyslexic At this time fMRI analysis is strictly a research procedure and is not used for diagnostic purposes.
Why Use The Reading Skills Profile Method?
The other methods have flaws, are difficult and expensive to administer, need to be administered by specialists, and do not give timely results. As an example, The RTI method can take three years to make a diagnosis.
Advantages of the Reading Skills Profile Method
- Performed by computer using WEB based applications
- Can be performed at any location that is relatively quiet
- No specialists needed to administer testing
- Analysis is performed by highly sophisticated computer algorithms
- A detailed report is generated immediately that is readable by a non-professional
- Analysis may rule out dyslexia but identify a different reading problem
- Frequent follow-up testing permits tracking reading progress


 Facebook
Facebook
 Yelp
Yelp